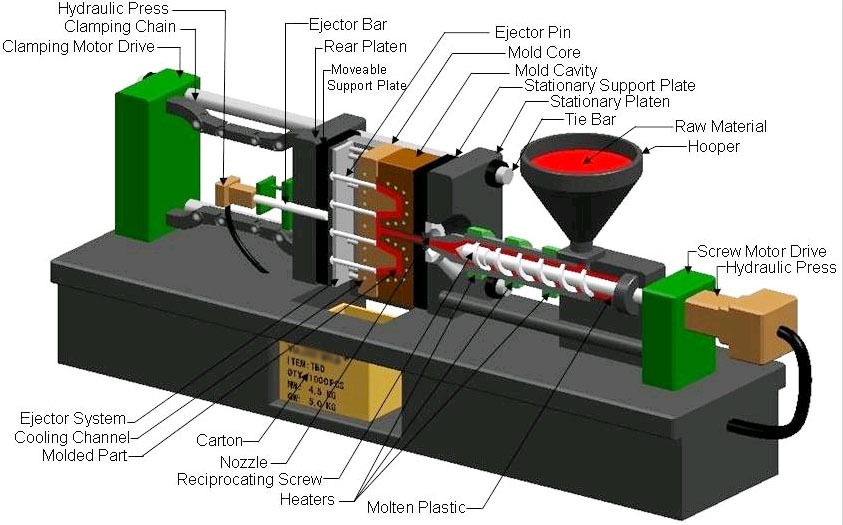
In the world of manufacturing, injection moulding is a widely used process for producing plastic parts. It involves injecting molten plastic into a mould cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify, and then ejecting the finished part. But what material is used in injection moulding? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the top materials commonly used in injection moulding, their properties, applications, and brand names.
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic, also known as poly(methyl methacrylate) or PMMA, is a strong and transparent thermoplastic that serves as a lightweight alternative to glass. It offers excellent optical clarity, allowing a high percentage of light to pass through. Acrylic is resistant to ultraviolet (UV) light and weather conditions, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it is not resistant to solvents and can be easily stained by greases and oils.
Applications for acrylic injection moulding include windows, greenhouses, solar panels, and other transparent components for architectural, lighting, and outdoor applications. Some popular brand names for acrylic plastics include Trinseo PLEXIGLAS® and DuPont LUCITE®.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, commonly known as ABS, is a versatile thermoplastic that is easy to mould. It has a relatively low melting point, which allows for easy processing and the incorporation of colorants, textures, and surface finishes. ABS is known for its strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for various applications. However, it is not recommended for outdoor use, as it lacks resistance to sunlight and weather conditions. ABS is commonly used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and industrial fittings. Popular brands of ABS include Samsung Starex®, Toray Toyolac®, BASF Terluran®, and Ineos Lustran®.
Nylon (Polyamide, PA)
Nylon, also known as polyamide (PA), is a synthetic polymer that combines toughness, high heat resistance, and abrasion resistance. It has good fatigue resistance and noise-dampening properties. Nylon is not inherently flame-resistant, but flame-retardant versions are available. However, it is susceptible to degradation from sunlight unless a UV stabilizer is added. Nylon provides poor resistance to strong acids and bases.
Nylon is used for a wide range of applications, including mechanical parts such as bearings, bushings, gears, and slides. It is also used in casings, snap-fit closures, threaded inserts, and jigs and fixtures. Some popular brands of nylon include Nylon 11, Nylon 12, Nylon 46, and Nylon 66. Glass-filled nylon is also available for greater mechanical strength.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a strong, lightweight, and transparent plastic material. It has excellent optical properties, allowing for light transmission while maintaining its color and strength when pigmented. Polycarbonate is stronger than glass and highly durable. It is also resistant to impact and has a wider temperature range compared to other plastics. However, polycarbonate contains bisphenol A (BPA), so it is not recommended for food preparation or storage. Popular brands of polycarbonate include SABIC Lexan® and Covestro Makrolon®.
Applications for polycarbonate injection moulding include machinery guards, windows, diffusers for LEDs, and clear molds for urethane and silicone casting. Polycarbonate is also used in the automotive industry for parts such as headlamp lenses and interior trim.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is the most commonly used plastic in the world. It comes in different grades based on its density, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyethylene is resistant to moisture and chemicals, but its outdoor applications are limited due to poor UV resistance. HDPE and LDPE are not suitable for high-temperature applications. PET, on the other hand, can be clear and is commonly used in beverage bottles.
Polyethylene injection moulding is used in a wide range of products, including housewares, toys, food containers, and automotive parts. Popular brands of polyethylene include BASF and DuPont.
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyoxymethylene, also known as acetal or POM, is an engineering plastic with excellent rigidity, thermal stability, and low friction coefficient. It has low water absorption and good chemical resistance. POM is naturally opaque and white in color. It can be reinforced with fiberglass or minerals for improved strength and stiffness. However, POM lacks resistance to sunlight and has relatively high shrinkage during injection moulding. Popular brands of POM include DuPont Delrin® and Ensinger TECAFORM®.
POM injection moulding is used in a wide range of applications, including bearings, gears, conveyor belts, pulley wheels, fasteners, eyeglass frames, and high-performance engineering components.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is the second most commonly used plastic in the world. It provides good chemical resistance, retains its shape after torsion or bending, and has a high melting point. Polypropylene is not resistant to UV light and degrades into harmful aromatic hydrocarbons at high temperatures. It is also difficult to bond and paint. Polypropylene injection moulding is used in products such as toys, storage containers, sporting goods, and power tool bodies. Some popular brands of polypropylene include Basell PP, ExxonMobil PP, and Formosa PP.
Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene plastics are lightweight, inexpensive, and resistant to moisture and bacterial growth. There are two main types of polystyrene: general-purpose polystyrene (GPPS) and high-impact polystyrene (HIPS). GPPS is brittle and has less dimensional stability than HIPS, which is compounded with butadiene rubber to enhance its material properties. Polystyrene injection moulding is used in various applications, including medical, optical, electrical, and electronic applications. Some popular brands of polystyrene include American Styrenics PolyRenew® and BASF Polystyrol®.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) is a blend of plastic and rubber materials. It has the properties and performance of rubber but can be processed like plastic. TPE can be stretched and returns to its original shape upon the removal of stress. It is also recyclable. TPE injection moulding is used in footwear, medical devices, auto parts, and pet products. ISO 18064 defines generic classes of commercial TPEs, and there are various manufacturers and brand names available.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is a type of TPE that is often considered separately due to its popularity. It has a rubber-like elasticity and can substitute hard rubber due to its higher durometer. TPU has good load-bearing capabilities and can withstand exposure to ozone, extreme temperatures, and chemicals. TPU injection moulding is used in footwear, gaskets, caster wheels, and sporting goods, as well as cases or enclosures for electronics and medical devices. Different classes of TPU materials are available, including polyester, polyether, and polycaprolactone.
In conclusion, injection moulding is a versatile manufacturing process that can utilize a wide range of plastic materials. Each material has its own unique properties, applications, and brand names. Understanding the characteristics of these materials can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right material for your injection moulding project. Whether you need transparency, impact resistance, chemical resistance, or other specific properties, there is a material that can meet your requirements. Partnering with experts in injection moulding, like Fictiv, can help ensure a successful and efficient production process.





